Ønsker du mer info og pris?
IC solutions for earthquake and stairs in buildings
ISSUES RELATED TO EARTHQUAKES
RELATIVE DISPLACEMENT BETWEEN STORIES
Different Building Standards vary regarding how much buildings can move, but this can be up to 3% of the
height of the building. Therefore, if a building is 200 metres tall, it can move laterally +/-6 metres at the top.
Among other concerns, this movement can have serious consequences for the stairs in the building.
The difference in horizontal displacement between two stories can create a significant change to the length of
the diagonal line spanned by the stairs.
Figure 2 illustrates a straight stair with a mid-height landing. With a typical story height of 3 metres, the
horizontal distance between the anchorage points can vary +/- 90mm (3000mm x 3%).
In one deformation cycle, the relative displacement between stories causes the stair to compress, which
potentially causes plastic (permanent) deformation of the stair. In the next cycle the span length of the stair
increases which may result in an insufficient support width of the stair and the stair collapses.
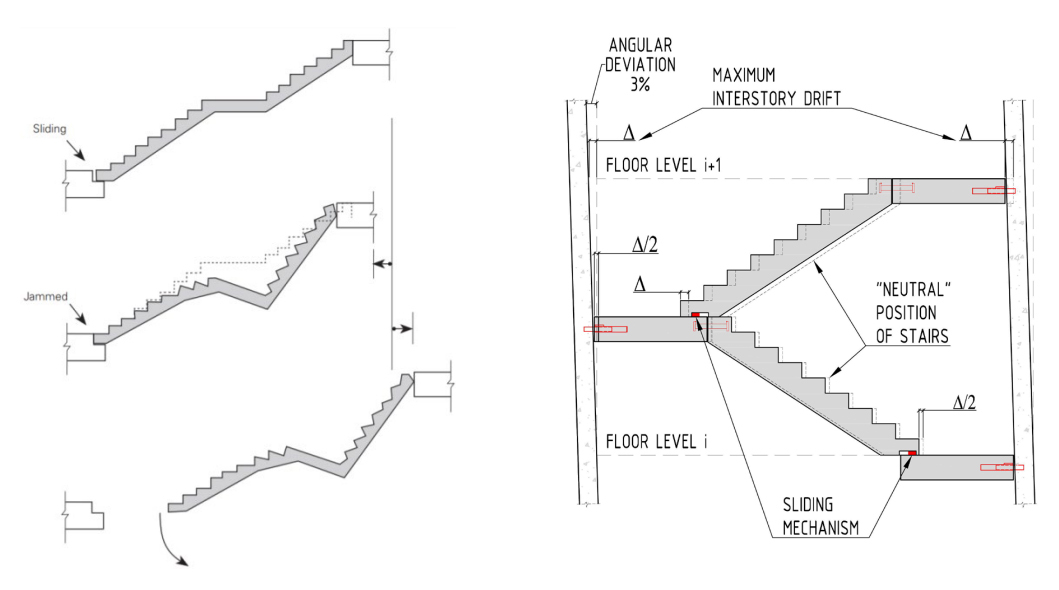
Figure 2: Relative displacement between stories gives a permanent shortening followed by a collapse /1/.
Figure 2, right side, illustrates a typical stair shaft with “scissor” stairs, where the stair turns back 180 degrees
at the mid-height landing. Assuming a storey height of 3m, means the distances between the supports may
vary +/- 45mm (1500mm x 3%). The sliding mechanism at the bottom of the stair must allows for the relative
displacement.
Technical information download
Seismic zones TSS - RVK
| Memo no | Name/download | Format | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcyl, Earthquake. | Excel |  | |
| Des Bull | Des Bull Report. |  | |
| Analyses of stairwells performace and damage during Wenchuan earthquake. |  | ||
| Memo no 70 | Memo 70 i C SOLUTION FOR EARTHQUAKE AND STAIRS 2 |  | |
| Memo no 71 | iC solution for earthquake and stairs spreadsheet. |  | |
| Memo no 72 | iC solution for earthquake and stairs additional reinforcement. |  |